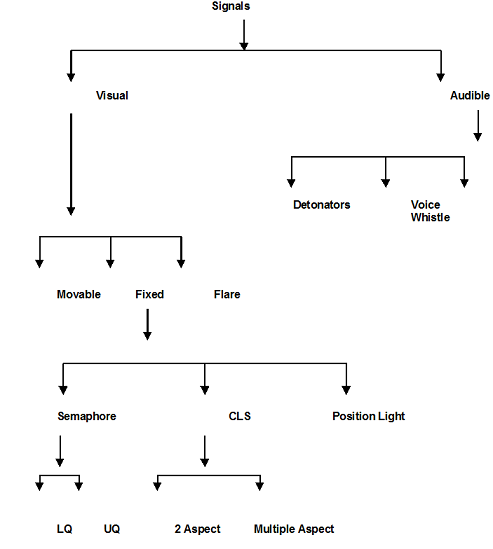
NECESSITY OF SIGNALS
Signaling Concepts :
- Railway vehicles move on steel rail track and engines, wagons and coaches are provided with flanged steel wheels.
- The rolling of steel wheels on the steel rail has the least friction and therefore, it is the most efficient means of locomotion.
- Unlike road vehicles, railways have no capacity to steer away. They have to follow a fixed path, as guided by these rails. They are required to follow one another.
- Precedence and crossings can be arranged only at the station. Drivers of a locomotive have only control over the speed of the train, he can start and stop. This communication to the driver to proceed or to stop is through signals.
What are Signals:
The signal is medium to convey a particular predetermined meaning in non-verbal form. Signals of the non-verbal form are also used in road transport, navy and air traffic control etc.
Fixed Signals :
- A signal of fixed location indicating the condition affecting the movement of the train. It includes Semaphore arm, or a disc or fixed light used by day or night.
- Semaphore is a Greek word. SEMA stands for Sign, PHERO means bear.
- Semaphore signal is rectangular or fishtailed at the end. Fixed on a vertical post, kept horizontal.
- Easily distinguishable from longer distances.
There are three methods of display:
- Vertical – Parallel to post.
- Midway Position – below horizontal
- Midway Position – above horizontal.
Various Forms of Signals :