Fire Safety:
INTRODUCTION:
Fire serves as an obedient servant when handled properly. But it behaves like a monster when handled in a careless manner. Hence it is necessary that a person working especially in hazardous environments should know about the basic concepts of fire and its prevention measures/extinguishers. This report will give a reasonably good insight on FIRE, the different type of fire extinguishers and its use, and important measures to prevent the occurrence of unwanted fire.
CONCEPT OF FIRE:
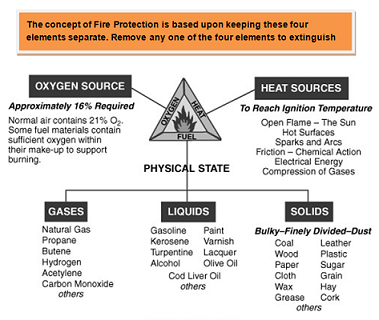
Fire results due to combustion of fuels (combustible materials ) in the presence of air or oxygen. In order that a fire gets started there should initially be sufficient heat to ignite the fuel, and for the fire to sustain, the combustion reaction should produce enough heat to maintain the fuel temperature above its ignition temperature. In a nutshell, for a fire to break out the following three components are essential:
- FUEL
- OXYGEN(AIR)
- HEAT
These 3 components are shown as the 3 sides of a triangle (known as FIRE TRIANGLE) indicating thereby that all the three components should come in contact with each other for a fire to happen.
FIRE TRIANGLE :
It is now recognized that in addition to the above three elements, there is a chain reaction taking place during combustion. In order to sustain the combustion, the chain reaction should continue. Hence in place of the standard fire triangle, the elements of combustion are also represented, in the form of a tetrahedron, the 4th side of which represents the uninhibited combustion chain reaction, in place of the standard fire triangle.
Interrupting the reaction:
Recent studies in fire chemistry have resulted in certain revisions and expansions in the theories of fire extinguishers. In analyzing the anatomy of fire, the original fuel molecules appear to combine with oxygen in a series of successive intermediate stages, called branched-chain reactions, in arriving at the final end products of combustion. It is these intermediate stages which are responsible for the evolution of flames.
As molecules fragmentize in these branched chain reactions unstable intermediate products called free radicals are formed. The concentration of free radicals is the determining factor of flame speed. The life of the free hydroxyl radical is very short, being in the order of 0.0001 seconds, but long enough to be of vital importance in the combustion of fuel gases. The almost simultaneous formation and consumption of free radicals appear to be the lifeblood of the flame reaction.
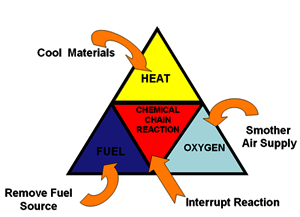
It is the free radicals in these branched chain reactions which are removed from their normal function as a chain carrier by dry chemical and halogenated hydrocarbon extinguishing agents.The Fire prevention and extinguishing technology are based on the principle involved in the above triangle tetrahedron. If any one component is separated from these, the fire can be extinguished.
Preventive action Fire extinguished :
- Removal of the fuel Starvation
- Stoppage of oxygen/ Air Blanketing/Smothering
- Removal of Heat Cooling
- Removal of free radicals Breaking the chain reaction
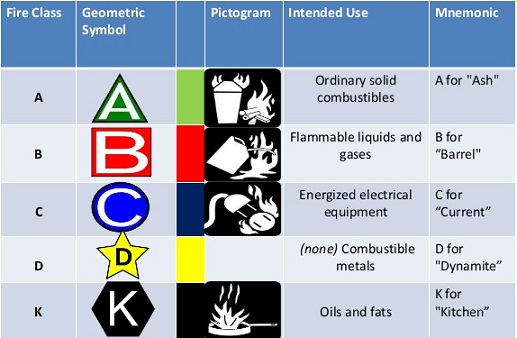
CLASSIFICATION OF FIRE:
Fires have been classified into 5 classes, based on the nature of materials involved in combustion. Details of these classes and the extinguishing medium to be used for fighting them are given in Table-1. However, the latest classification of fire recognizes only four classes, since the fifth one (class E) involving electrical/electronic equipment will be changed to class A or B when the current is switched off.
FIRE EXTINGUISHERS:
In the case of major fires, use of automatic sprinkler system, deluge system, and fire hydrants, fire tenders etc. are involved together with professional expertise for firefighting. But it is a known fact that all major fires , except those involved with some kind of explosives, start from minor fires initiated by either direct heat, electric spark or any other ignition sources. Many fires give an indication in the initial stages itself in the form of a smoke. If the fires are noticed early then spreading can be easily prevented. Action taken either to control or extinguish the fire at the incipient stages itself before it spreads is called first aid firefighting and equipment used for this purpose are called first aid fire fighting appliances. To facilitate easy extinguishment at the incipient stages portable extinguishers are employed.
PORTABLE FIRE EXTINGUISHERS:
A portable fire extinguisher is designed for the discharge of a contained amount of fire extinguishing agent at the will and direction of a human operator. Such a device can either be easily carried to the scene of fire or wheeled on a mobile carrier. Successful utilization depends on
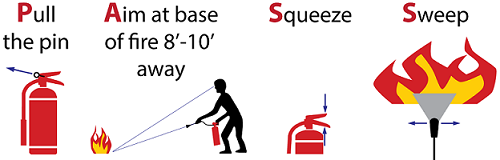
- The proper choice of extinguisher and extinguishing media.
- Knowledge of the correct technique of application
- Adequacy of extinguishing agent
- The proper functioning of the device as influenced by its design and maintenance
Since all fires having the potential of developing into major fires can be averted if put out at the initial stages itself. It is essential that all personnel working in the areas should be able to operate the extinguishers correctly.Different types of fire extinguishers are available where different kinds of extinguishing mediums are employed. These are used depending on the class of fire. The oldest form of portable extinguisher is the fire bucket which is still commonly used for class ’A’ fire.
DRY CHEMICAL POWDER EXTINGUISHER:
These type of extinguishers are suitable for tacking petroleum fires, gas fires, fires in electrical appliances. They are noted for the speed with which they extinguish the fires. It extinguishes the fire by breaking the chain reaction. These extinguishers are available in 1,2,5, and 10 kgs capacities.
The principle of extinguishment:
These powders, mainly sodium bicarbonate, potassium bicarbonate and ammonium phosphate base and when applied to fire undergo the chemical reaction. The products thus formed will combine with the free radicals formed during the fire and thus prevent the chain reaction which is responsible for sustaining any fire.
CARE AND MAINTENANCE OF FIRE EXTINGUISHERS:
In order that firefighting equipment is to be used at instant notice, these must be always maintained in good working condition. The routine maintenance and test recommended and their periodicity for the different type of extinguishers are given below:
Once in a quarter:
- Withdraw the gas cartridge and check if the sealing disc is intact. Weigh the cartridge and compare it with the weight marked on the body. If the loss is 10%or more replace it with a fully charged one.
- Check the piercing mechanism for its proper working
- Remove the inner shell and clean portholes.
- Check the powder for granulation and caking. If caking is observed, charge it with the fresh charge.
Once in a year:
- 20% of the extinguisher should be operated and see for their performance.
Once in 5 years:
- Every extinguisher should be discharged at least once I 5 years.
- The hydraulic test should be carried out at a pressure of 31.5 kg/cm2. Before recharging, the extinguisher should be dry.
PRACTICAL HINTS ON FIRE PREVENTION:
Identification of ignition source via unextinguished cigarette butts, burning fuels, welding brazing flame, lighted matchsticks, overheating of heating elements or overloading or use of substandard electrical cables, and removing/avoiding them.
Incorporation of safety measures in building construction viz; provision of adequate fire resistance in the structural elements and proper selection of construction materials.Adequate exit doors during fire emergency and provision for lightning protection.
Housekeeping:
- Good housekeeping minimizes fire risk. Following important points contribute to good housekeeping.
- Laying on electrical wires in an orderly manner.
- No accumulation of waste materials in work areas.
- Electrical mains should be easily accessible.
- Dry grass and bushes around the building should be cleared regularly.Floors, steps, and stairs are free from obstruction.